Published On Nov 7, 2017
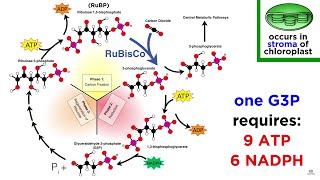
The Calvin Cycle or the Light independent reactions of photosynthesis are chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose. These reactions occur in the stroma, the fluid-filled area of a chloroplast outside of the thylakoid membranes. These reactions take the products (ATP and NADPH) of light-dependent reactions and perform further chemical processes on them. There are three phases to the light-independent reactions, collectively called the Calvin cycle: carbon fixation, reduction reactions, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration.
The Calvin cycle, Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) cycle, reductive pentose phosphate cycle or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic organisms.
The cycle was discovered by Melvin Calvin, James Bassham, and Andrew Benson at the University of California, Berkeley[3] by using the radioactive isotope carbon-14.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages in a cell. In the first stage, light-dependent reactions capture the energy of light and use it to make the energy-storage and transport molecules ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle uses the energy from short-lived electronically excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds[4] that can be used by the organism (and by animals that feed on it). This set of reactions is also called carbon fixation. The key enzyme of the cycle is called RuBisCO. In the following biochemical equations, the chemical species (phosphates and carboxylic acids) exist in equilibria among their various ionized states as governed by the pH.