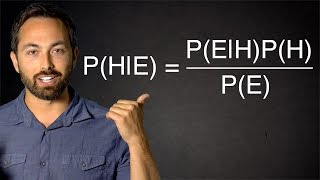Published On Sep 29, 2024
A Venn diagram is a way of visually organizing information to show how different groups of things relate to each other. It’s made up of overlapping circles, with each circle representing a different group or category.
Key Ideas:
1. Circles Represent Groups: Each circle in the Venn diagram stands for a group of things that share a common property.
• Example: One circle could be “fruits,” and another could be “red objects.”
2. Overlapping Areas: When two circles overlap, the area they share represents items that belong to both groups.
• Example: The overlap between “fruits” and “red objects” might include things like “apples” or “strawberries,” which are both fruits and red.
3. Non-Overlapping Areas: If part of a circle doesn’t overlap with another, it shows that those items only belong to one group.
• Example: In the “fruits” circle, bananas would be outside the overlap because they are fruits but not red.
4. Entire Diagram: The entire Venn diagram shows how all the groups relate to each other. It helps you see:
• Which items belong to just one group.
• Which items belong to multiple groups.
• Which items don’t belong to any group at all (those would be outside the circles).
A Venn diagram is useful for comparing and contrasting different groups, helping to clearly see similarities, differences, and shared properties.
Using Venn Diagrams in Problem Solving:
In mathematics, especially in probability and logic, Venn diagrams can help solve problems by visually breaking down how sets interact. For example:
• Counting Elements in Sets: Suppose you know the number of students who play basketball, soccer, and volleyball, and the number of students who play multiple sports. A Venn diagram can help you figure out how many students play exactly one sport, two sports, or all three.
• Probability: Venn diagrams are often used to represent probabilities of events. For example, if Set A represents an event like “rain” and Set B represents “wind,” their overlap might represent the probability of both rain and wind happening simultaneously.
#venn #venndiagram #set